Matlab BioSigKit Toolbox
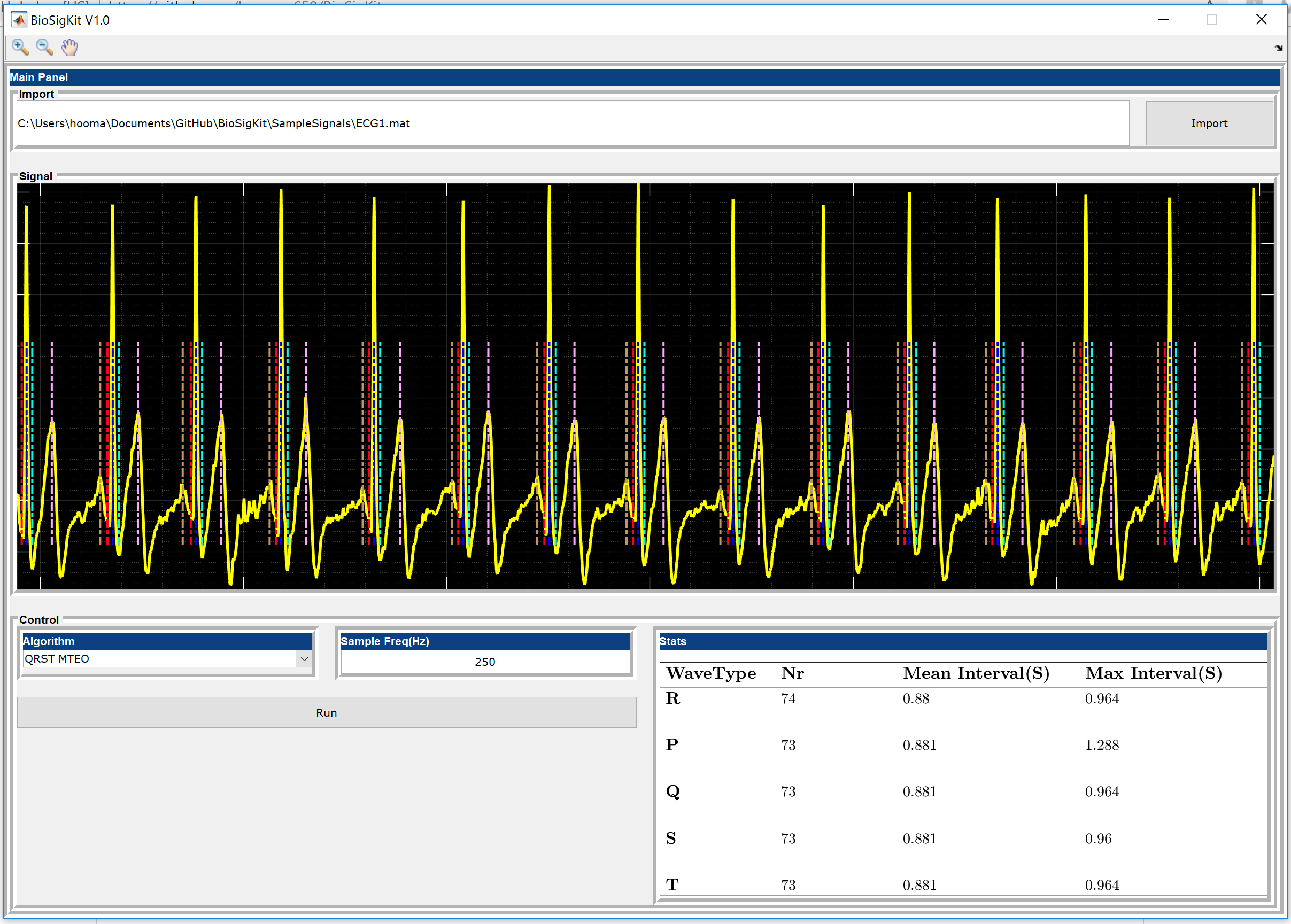
BioSigKit
In this post, I briefly introduce BioSigKit toolbox. BioSigKit is a set of useful signal processing tools in Matlab that are either developed by me personally or others in different fields of biosignal processing. BioSigKit is a wrapper with a simple visual interface that gathers this tools under a simple easy to use platform. BioSigKit’s goal is to create an open source platform and umbrella for the implementation and analysis of useful signal processing algorithms. All of it’s subroutines are implemented in pure MatLab script for the educational purposes even the most popular algorithms such as (Pan-Tompkins).
The ultimate goal of BioSigKit is not to be only used for ECG processing, it aims to be helpful in analysis of several different physiological signals such as EMG, ACC and EDR as well. For instance the last subroutine which is a general peak detector can already be used in many different signals even with low frequencies (Please see the paper by Scholkmann). BioSigKit offers other subroutines for ECG-derived respiration computation, real time multi-channel and single channel Foetal ECG extraction based on non-linear filtering and neural PCA. BioSigKit also offers Psuedo-correlation template matching which has proven to be more accurate for locating MUAPs in EMG signals (EMG toolbox (offered by the same author)). Futhermore, several more subroutines enable the user to estimate the posture of the subject from 3 channel ACC recordings, as well as ACC-derived respiration estimation. Please see the cheatSheet.pdf for the list of all methods provided by BioSigKit.
If you like what I do and want to support my efforts, please feel free to donate a cup of coffee!
QRS Detection Algorithms offered by BioSigKit
BioSigKit provides a set of subroutines implementing the six following QRS detection algorithms:
Pan and Tompkins [J. Pan, 1985;H. Sedghamiz, 2014]: This algorithm is probably one of the most widely used algorithms for QRS detection in the research community. It combines a set of preprocessing methods in order to enhance the detection rate and reduce the false detection of T-waves in the ECG recordings (subroutine name : BioSigKit.PanTompkins()).
Nonlinear Phase Space Reconstruction [J. Lee, 2002]: This method employs the area under the non-linear phase space reconstruction of the ECG recording in order to identify the QRS complexes (subroutine name : BioSigKit.PhaseSpaceAlg()).
State-Machine [H. Sedghamiz, 2013]: This algorithm employs state-machine in order to identify R, S and T waves in an ECG recording (subroutine name : BioSigKit.StateMachine()).
Filter Bank [V. Afonso, 1999]: The filter bank method combines several band-pass filters in order to better delineate the QRS complexes. This algorithm is very similar to wavelet based QRS detectors (subroutine name : BioSigKit.FilterBankQRS()).
QRS Multilevel Teager Energy Operator (MTEO) [H. Sedghamiz, 2016]: This algorithm employs Multilevel Teager Energy Operator (MTEO) in order to locate the QRS complexes. MTEO has been successfully used in Electromyography signals for action potential detection [H. Sedghamiz, 2016] since it is computationally much more efficient than wavelet transform (subroutine name : BioSigKit.MTEO_qrstAlg()).
Automatic Multiscale-based Peak Detection [Scholkmann2012]: This method is a more general peak detection. However, according to the study by Scholkmann et al. [Scholkmann, 2012], it showed a high performance for the beat detection as well. Therefore, it is implemented as one of the subroutines in BioSigKit (subroutine name : BioSigKit.AMPD_PAlg()).
Subroutines offered for analysis of ACC, EMG, EEG and Foetal-ECG
Activity detection with hilbert transform in EMG and audio signals (obj.Env_hilbert()). For more details regarding this algorithm see [Alarm detection].
Mobility and complexity computation with Hjorth parameters in EEG signals (obj.ComputeHjorthP). For more details regarding this subroutine refer to [Hjorth Parameters].
Posture detection and adaptive filtering in 3 Channel Accelerometer signals (obj.ACC_Act). This subroutine is able to compute the Energy Expenditure (EE) and Signal Magnitude Area (SMA) from 3 channel ACC recordings. Based on EE and SMA, the subroutine is able to estimate the activity level of the subject (e.g. steady, active, highly active). Accelerometers are used in many studies and being able to estimate the state of the subject by analyzing the ACC signals is helpfull in many tasks.
Accurate template matching for locating MUAPs in EMG recordings based on Psuedo-Correlation (obj.TemplateMatch). Psuedocorrelation has shown to be more accurate than Pearson correlation. For more details see [H. Sedghamiz, 2016].
Computation of ECG derived respiration based on real time neural PCA computation ([Neural PCA]). This subroutine first applies pan-tompkins algorithm to locate the R peaks and then reconstructs the EDR signal by computing the PCs of the QRS complexes in real-time (obj.EDR_comp).
Foetal-ECG extraction from multichannel and single channel maternal ecg recordings. BioSigKit implements a non-linear phase space filter that is able to extract foetal ecg recordings. This is based on delayed phase space reconstruction of the signal. For more details see [Schreiber, 1996]. Futhermore, it is possible to extract the foetal ecg in real-time with the neural PCA offered in BioSigKit. See demo.m file for more details (obj.nonlinear_phase_filt).
ECG artifact removal with Recursive Least Squares filter (RLS). BioSigKit also offers a subroutine to remove artefacts from ECG recordings by using a 3 channel Accelerometer recording with RLS filter (obj.adaptive_filter). BioSigKit also implements Adaptive Line Enhancer and its leaky version. For more details regarding motion artefact removal in ECG with ACC see [Shing-Hong Liu, 2009]
Getting Started and Installation
To install BioSigKit simply:
-
Download the repository.
-
Unzip the downloaded package and simply run “RunBioSigKit.m”.
-
See the instructions bellow for further details:
For help, type help BioSigKit.
BioSigKit might be used either from the command line or its Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Command Line :
To use the command line simply call the constructor as follows:
analysis = RunBioSigKit(InputSig, SampleFreq, 0);
To access subroutines simply use the point operator as :
analysis.PanTompkins();
The results are stored in the result struct, you can access it as :
analysis.Results;
Depending on the processing algorithm employed, the result struct would contain ‘P’, ‘Q’, ‘R’, ‘S’ and ‘T’ wave indices.
To see the list of all the subroutines and children accessible simply call analysis in Matlab command-line.
GUI :
To instantiate the GUI, simply run the RunBioSigKit().
Please note that GUI has only been tested on windows platforms and not Unix.
Examples :
See the Demo.m for a few examples on how to use BioKitSig.
Test Cases
BioSigKit comes with two sample ECG recordings for testing of the algorithms offered. See SampleSignals ECG1 and ECG2 for these test cases. Please use the GUI and simply choose the algorthim that you would like to evaluate to see the results. Furthermore, see the publications for each subroutine to get a better overview what the accuracy of the proposed method might be.
How to Cite
Sedghamiz, (2018). BioSigKit: A Matlab Toolbox and Interface for Analysis of BioSignals. Journal of Open Source Software, 3(30), 671, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.00671
Codemap
|--- RunBioSigKit.m <-------- Main module, GUI and Commandline
|--- CheatSheet.pdf <-------- Detailed helper file and subroutines of BioSigKit
|--- @BioSigKit <-------- Main module BioSigKit class
|--- BioSigKit.m <-------- BioSigKit object, instantiates all subroutines
|--- BioSigKitPanel.m <-------- Creates the Visualization panel and its controls
|--- Algorithms <-------- List of all subroutines offered by BioSigKit
|--- AMPD_P.m <-------- Multi-scale Peak detector algorithm
|--- MTEO_qrst.m <-------- Multilevel Teager Energy Operator
|--- PhaseSpaceQRS.m <-------- Phase Space based QRS detector
|--- SimpleRST.m <-------- State machine for R, S and T peak detection
|--- distingusihable_colors.m <-------- Computes distinguishabe colors for visualization
|--- nqrsdetect.m <-------- Filter Bank ECG detector
|--- pan_tompkin.m <-------- Pan Tompkins implementation
|--- phasespace.m <-------- Computes phase space of a signal
|--- ACC_Activity.m <-------- Posture estimation in ACC recordings
|--- ALE_imp.m <-------- Delayed adaptive line enhancer
|--- envelop_hilbert.m <-------- Alarm detection with hilbert transform (EMG, Audio, ECG)
|--- energyop.m <-------- Teager energy operator
|--- NLMS_ecg.m <-------- ECG artefact removal with ACC recordings
|--- projective.m <-------- Nonlinear delayed phase-space filtering
|--- PsC.m <-------- Psuedo-correlation for template matching
|--- RLS.m <-------- Recursive Least Squares filter
|--- RTpca.m <-------- Real-time neural PCA
|--- VLALE_imp.m <-------- variable leaky ALE filter
|--- layout <-------- Dependencies for GUI (third party)
|--- SampleSignals <-------- Test Cases
|--- ECG1 <-------- test case 1 for evaluation of the algorithms
|--- ECG5 <-------- test case 2 for evaluation of the algorithms
|--- Foetal_ecg <-------- 8 channel maternal ECG recordings
|--- ACC <-------- 3 channel Accelerometer recordings
|--- paper <-------- Details the toolbox